
As long as total fixed and variable costs equal total revenue, the company will break even. Divide fixed costs by the revenue per unit minus the variable cost per unit. The fixed costs are those that do not change, no matter how many units are sold. Revenue is the price for which you’re selling the product minus the variable costs, like labor and materials. The break-even point formula is calculated by dividing the total fixed costs of production by the price per unit less the variable costs to produce the product. The Break Even Revenue Calculator is a vital tool for understanding how much revenue you need to generate in order to cover your operating expenses.
Using break-even analysis to determine level of production
For more cost cutting ideas, check out our guide of 25 ways to cut costs. The magic happens when our intuitive software and real, human support come together. Book a demo today to see what running your business is like with Bench. To get a better sense of what this all means, let’s take a more detailed look at the formula components. Central to the break-even analysis is the concept of the break-even point (BEP).
- Assume that an investor pays a $5 premium for an Apple stock (AAPL) call option with a $170 strike price.
- The break-even point (BEP) is the amount of product or service sales a business needs to make to begin earning more than you spend.
- A break-even analysis relies on three crucial aspects of a business operation – selling price of a unit, fixed costs and variable costs.
- It dictates everything from how to price your products to when it might be the right time to expand.
Help your small business stay profitable with better financial management
For example, you could decrease the required number of subscriptions to break even by reducing the variable costs (like using AI customer service). That’s the difference between the number of units required to meet a profit goal and the required units that must be sold to cover the expenses. In our example, Barbara had to produce and sell 2,500 units to cover the factory expenditures and had to produce 3,500 units in order to meet her profit objectives. It’s the amount of sales the company can afford to lose but still cover its expenditures.
Break-even Point Calculator
Consider the following example in which an investor pays a $10 premium for a stock call option, and the strike price is $100. The breakeven point would equal the $10 premium plus the $100 strike price, or $110. On the other hand, if this were applied to a put option, the breakeven point would be calculated as the $100 strike price minus the $10 premium paid, amounting to $90. If the price stays right at $110, they are at the BEP because they are not making or losing anything. Options can help investors who are holding a losing stock position using the option repair strategy.
Outsource fixed costs
Typically, this analysis works best for businesses that focus on a single product or service. The analysis becomes more complex and less accurate if you offer a wide range of products with different price points and variable costs. For example, If you sell both high-end electronics and low-cost accessories, a single break-even analysis won’t account for the differing profit margins. You’d need individual analyses for each product category to get a more accurate picture of your profitability. Assume a company has $1 million in fixed costs and a gross margin of 37%.
Contoh Studi Kasus BEP
Calculating the break-even point in sales dollars will tell you how much revenue you need to generate before your business breaks even. Here are four ways businesses can benefit from break-even analysis. This is a step further from the base calculations, but having done the math on BEP beforehand, you can easily move on to more complex estimates.
A breakeven point tells you what price level, yield, profit, or other metric must be achieved not to lose any money—or to make back an initial investment on a trade or project. Thus, if a project costs $1 million to garmin fenix 5 undertake, it would need to generate $1 million in net profits before it breaks even. If the stock is trading at $190 per share, the call owner buys Apple at $170 and sells the securities at the $190 market price.
Whether you’re trying to promote your brand-new product, stay ahead of your competitors, or cut down on your expenses, you need to have a strategy in place. This helps you craft a more formidable strategy and reap better benefits for your company. In our example above, Maria’s break-even point tells her she needs to create eight quilts a month, right? But what if she knows she can create only six a month given her current time and resources? Well, per the equation, she might need to up her cost per unit to offset the decreased production.
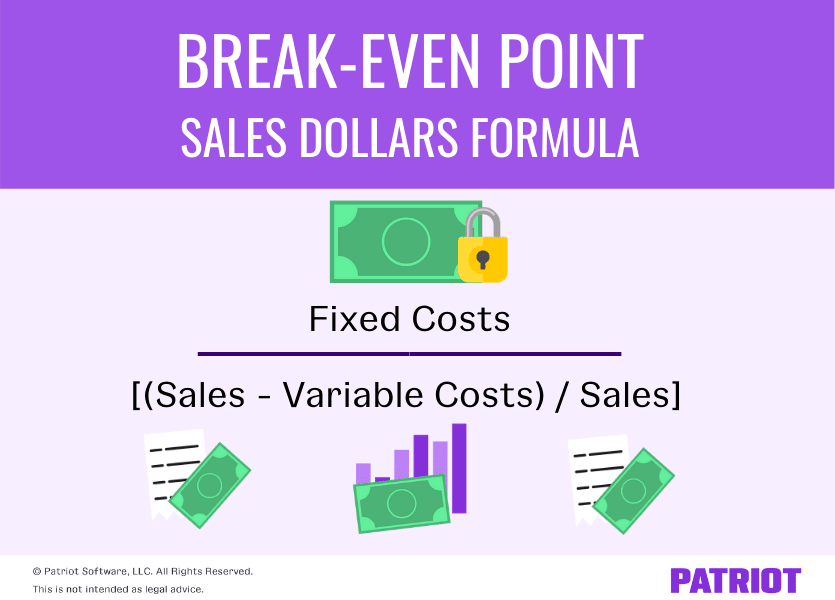
If you have any other costs tied to the products you sell—like payments to a contractor to complete a job—add them to your cost of goods sold to find your total variable costs. Your fixed costs (or fixed expenses) are the expenses that don’t change with your sales volume. Some common fixed costs are your rent payments, insurance payments and money spent on equipment. These costs will stay the same regardless of whether you sell one unit or a million units. When companies calculate the BEP, they identify the amount of sales required to cover all fixed costs before profit generation can begin. The break-even point formula can determine the BEP in product units or sales dollars.
Or, if using Excel, the break-even point can be calculated using the “Goal Seek” function. Our mission is to empower readers with the most factual and reliable financial information possible to help them make informed decisions for their individual needs. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
This formula helps you determine the total revenue required to cover your operating expenses, based on your business’s gross margin. One limitation of break-even analysis is that it assumes selling prices will stay the same over time. In reality, prices often fluctuate due to market conditions, competition, or changes in demand. For example, if you run a café, you might decide to lower the price of your best-selling drink to attract more customers. While this could boost foot traffic, it also means your break-even point will change and you’ll need to sell more drinks to reach profitability. Once you’ve determined your break-even point, you’ll be able easily view how many products you need to sell and how much you’ll need to sell them for in order to be profitable.
